#include<LiquidCrystal.h>
#define
moisture_sensorPin A0
#define
float_switchPin A1
#define motorPin 4
#define soil_statusPin
2
#define
tank_statusPin 3
LiquidCrystal
lcd(13,12,11,10,9,8);
const int
avg_moisture = 800;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
lcd.begin(16,2);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("
AUTOMATIC ");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("
IRRIGATION S/M ");
delay(2000);
pinMode(moisture_sensorPin,INPUT);
pinMode(float_switchPin,INPUT);
pinMode(motorPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(soil_statusPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(tank_statusPin,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(motorPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(soil_statusPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(tank_statusPin,LOW);
}
void loop()
{
lcd.begin(16,2);
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("
MOISTURE - ");
if(analogRead(moisture_sensorPin) >
avg_moisture){
lcd.print("HIGH");
digitalWrite(soil_statusPin,HIGH);}
if(analogRead(moisture_sensorPin) <
avg_moisture){
lcd.print("
LOW");
digitalWrite(soil_statusPin,LOW);}
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("TANK
LEVEL- ");
if(
digitalRead(float_switchPin) == HIGH){
lcd.print("HIGH");
digitalWrite(tank_statusPin,LOW);}
if(
digitalRead(float_switchPin) == LOW){
lcd.print("
LOW");
digitalWrite(tank_statusPin,HIGH);}
digitalWrite(motorPin,LOW);
if(analogRead(moisture_sensorPin)
< avg_moisture && digitalRead(float_switchPin) == HIGH)
{
while(analogRead(moisture_sensorPin) <
avg_moisture && digitalRead(float_switchPin) == HIGH)
{
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("
MOISTURE - LOW");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("
MOTOR IS ON ");
digitalWrite(soil_statusPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(tank_statusPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin,HIGH);
}
if(analogRead(moisture_sensorPin) >
avg_moisture){
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("
MOISTURE - HIGH");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("
MOTOR - OFF ");
digitalWrite(soil_statusPin,HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorPin,LOW);
delay(3000);}
if(digitalRead(float_switchPin) == LOW){
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print(" TANK
LEVEL- LOW");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("
MOTOR - OFF ");
digitalWrite(tank_statusPin,HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorPin,LOW);
delay(3000);}
}
delay(500);
}
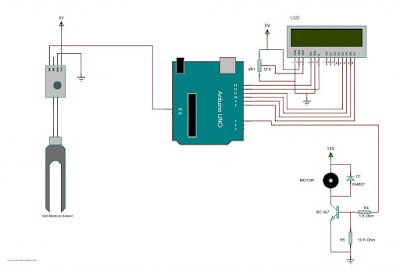
In this programming part, to facilitate communication between
Arduino and LCD module, we make use of a built in library in Arduino
<LiquidCrystal.h>.
The Arduino reads the sensor output through the analog input
pins using analogRead function. For example “analogRead(moisture_sensorPin);”
converts the voltage (in the range 0 to 5V) at the A0 pin into a number (in the range 0 to 1023)
This way the voltage at A0 is compared to a fixed number (avg_moisture) for
identifying the current status of the soil.